

There are 4 stages of binary fission which make up the process of cell division for. During the stationary phase the population grows slowly or stops growing because of decreasing food, increasing waste, and lack of space. Binary fission is the method of reproduction for asexual life forms.During the exponential growth phase (log phase) the population increases geometrically as long as there is sufficient food and space for growth.During the lag phase growth is relatively flat and the population appears either not to be growing or growing quite slowly as newly inoculated cells are adapt to their new environment.In a closed growth system, a bacterial population usually exhibits a predictable pattern of growth - its growth curve - that follows several stages or phases.Although bacteria are capable of replicating geometrically as a result of binary fission, this only occurs as long as their is space to grow, sufficient nutrients, and a way to dispose of waste products.The bacterial divisome is responsible for directing the synthesis of new cytoplasmic membrane and new peptidoglycan to form the division septum.Par proteins function to separate bacterial chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell during bacterial cell division.Because of binary fission, bacteria increase their numbers by geometric progression whereby their population doubles every generation time.For many bacteria the generation time ranges from minutes to hours. Generation time is the time it takes for a population of bacteria to double in number.Bacteria replicate by binary fission, a process by which one bacterium splits into two.The nuclear materials and necessary organelles are copied into each of the daughter cells.\)), although the rate of death depends on the degree of toxicity and the resistance of the species and viable cells may remain for weeks to months. A new cell wall is formed, and the cell splits at the center. The parent cell divides into two new daughter cells during this phase.The two chromosomes are also separated during elongation.
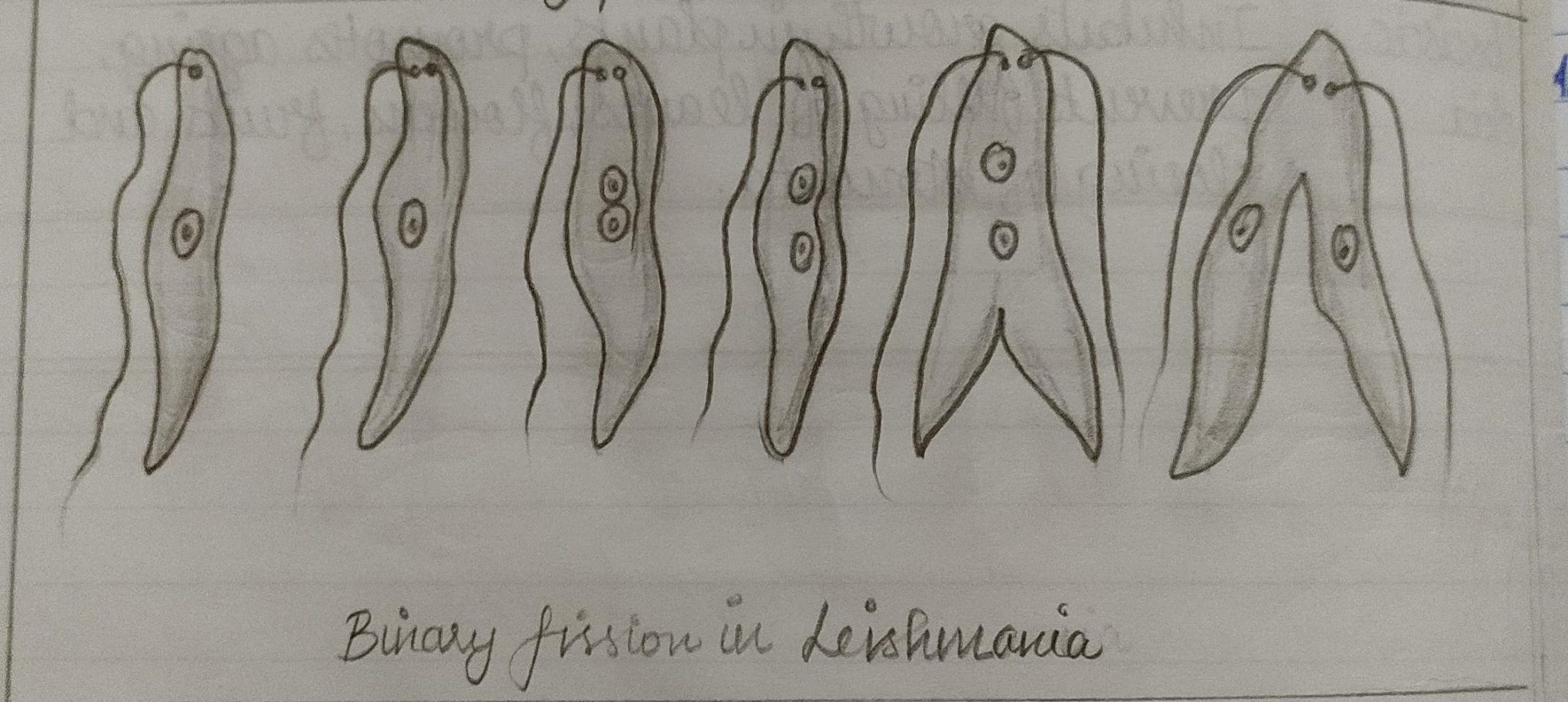
A septum, or division wall, begins to form in the middle of the cell during elongation. Elongation is a phase of the cell cycle in which the cell grows in length.Another sign that binary fission is about to occur is that the two strands of DNA start to migrate to opposite poles of the cell. Cytoplasmic content also starts to increase. After the chromosome is copied, the bacterium begins to grow in preparation for binary fissions.This process essentially doubles the bacterium’s genetic content. The bacterium uncoils, and then replicates its chromosome.The cell divides and the original and replicated chromosomes go to opposite sides. The single DNA molecule replicates and each copy attaches to the cell membrane. It’s similar to mitosis in eukaryotic cells, but there is no spindle apparatus formation. There are four main types of binary fission:Įach type involves a different orientation of the cell during division, and results in different shapes and sizes of the resulting cells. The main difference between the two processes is that binary fission occurs in prokaryotic cells while mitosis occurs in eukaryotic cells. Difference Between Binary Fission And Mitosisĭuring binary fission and mitosis, chromosomes are copied in order to create two new daughter cells.
This process is the simplest and most common method of asexual reproduction.Īmoeba is a single-celled organism that, similar to bacteria, creates new cells through binary fission.
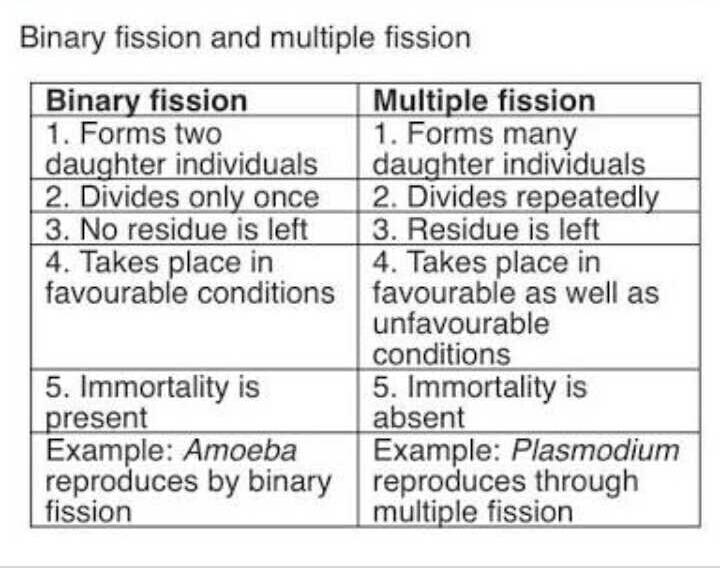
It Is called Binary fission because the organism splits into two during reproduction. Difference Between Binary Fission And Mitosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
